Last Updated on 25th April 2022
What is LiDAR data
What is LiDAR Data & How is it Used?
LiDAR systems use light pulses to collect information about landscapes, the earth’s surface, buildings and more. The information gathered by this method is collectively known as LiDAR data. It can be used for analysis, to create three-dimensional models, digital twins of buildings and landmarks, and much more. We’re going to dive into the ‘whats’ and ‘hows’ of LiDAR data to tell you all you need to know.
What is LiDAR Data?
LiDAR data is the information that a LiDAR system collects about the environment or area scanned. The data itself is a collection of points that signify the x, y and z coordinates of a single point in the area scanned. Point clouds collate all these points into one dataset.
What kind of data does LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) collect?
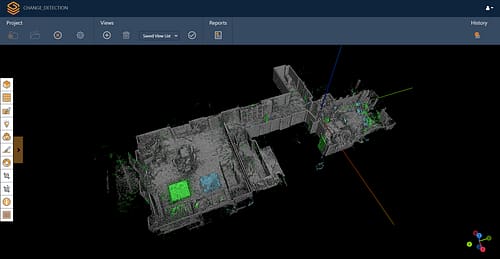
LiDAR data is collected as a point cloud. Each individual point reflected on the surface scanned forms a part of the data. LiDAR point cloud data can be minimal or vast, from a small floorplan to a map of an entire city.
How is LiDAR data collected?
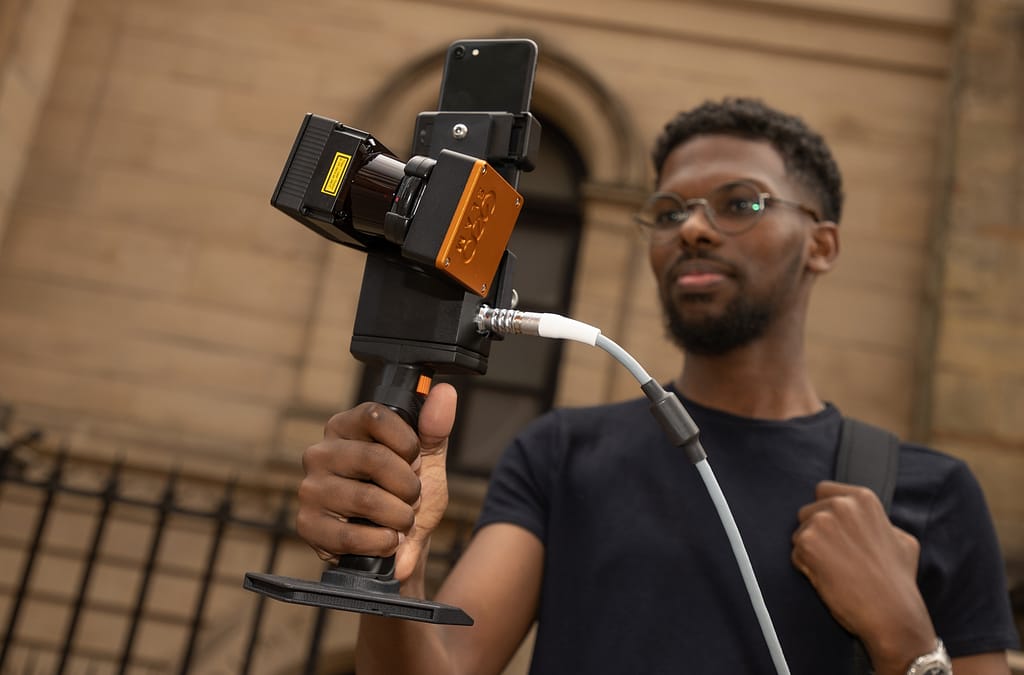
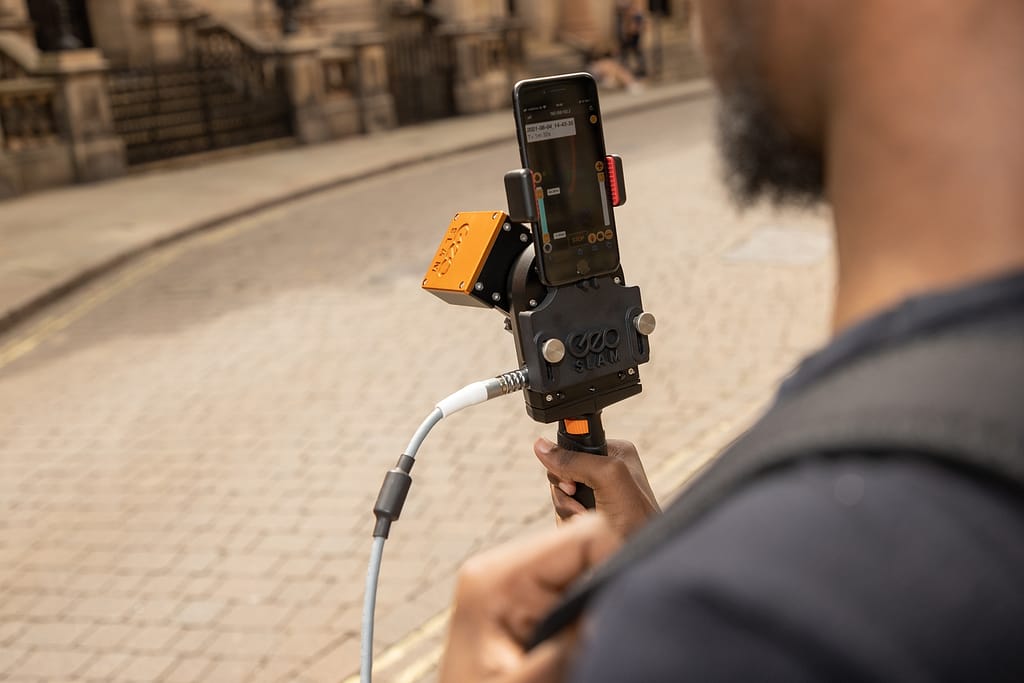
If you want to collect LiDAR data for yourself you’ll need the right equipment and technology. LiDAR systems are built to collect LiDAR data. Depending on the data you need, you could use a handheld LiDAR scanner on foot, airborne LiDAR, or a vehicle-mounted scanner. A laser scanner like our ZEB Go, ZEB Revo RT or ZEB Horizon is the ideal tool to use.



As you scan, a laser pulse is emitted and returns to the scanner. This simple process happens hundreds of thousands of times per second and the time it takes for each beam of light to return to the scanner is measured. This is known as a ‘Time of Flight’ measurement. This remote sensing method allows the LiDAR system to collect vast amounts of data in a short space of time.
One of the huge benefits of this method of data collection is that buildings and objects can be measured and surveyed in a non-intrusive way. It’s not necessary to shut down a busy site in order to get the data you need with a LiDAR sensor. Scanning using light pulses is quick and easy, and measurements are available very quickly.
How accurate is LiDAR data?
The average accuracy level for LiDAR data is +/- 1-3 centimetres. Point clouds are actually far more detailed and precise than any other survey methods, making 3D modelling and mapping much more prevalent than it was before this technology was developed.
How is LiDAR data stored?
Because point cloud data is so vast and detailed, the file sizes can be extremely large. The industry standard is to store it in a binary format called LAS. This format was created and maintained by the American Society for Photogrammey and Remote Sensing (ASPRS). This standard format allows the data to be interchanged whilst maintaining all the information required.
You might also be wondering where LiDAR data is stored. Data can be uploaded to processing software like GeoSLAM Connect, where it can be accessed by multiple team members, processed and archived. Using software like this you can choose where you want your processed data to be stored. It could be on a company network, or in a project collaboration tool like Google Drive, Dalux, BIM360 or Viewpoint 4projects.
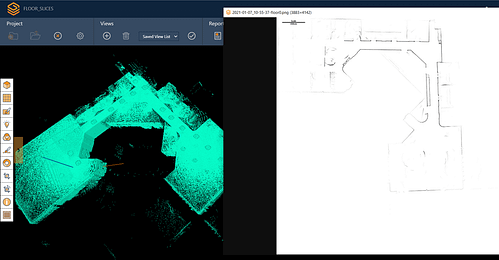
What does LiDAR data look like?
Most LiDAR data sets contain millions of different points. In its basic sense , your data would look like a collection of dots. Without colour or further detail this can be hard to interpret. However, there are plenty of ways to process this information to make it more meaningful.
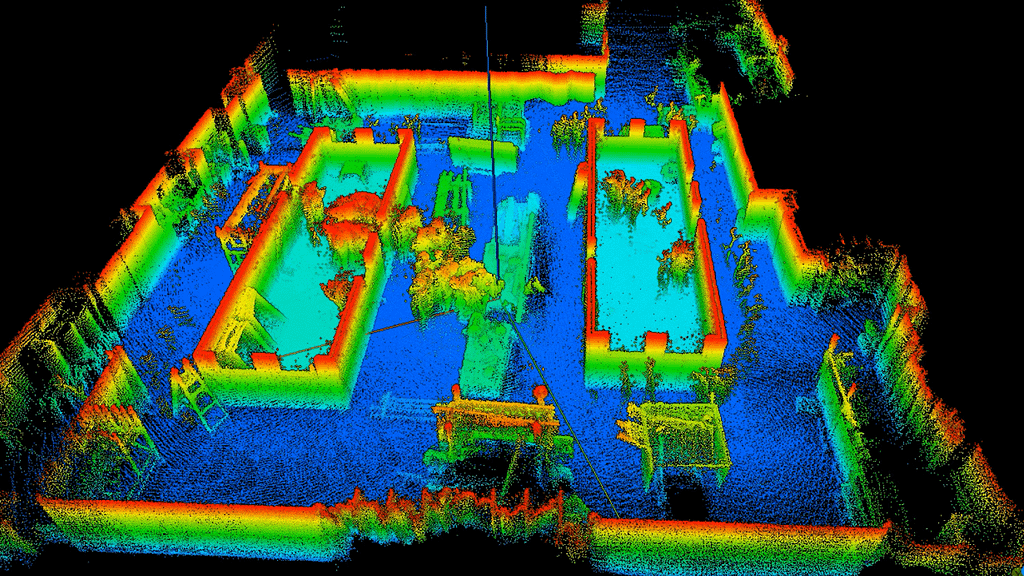
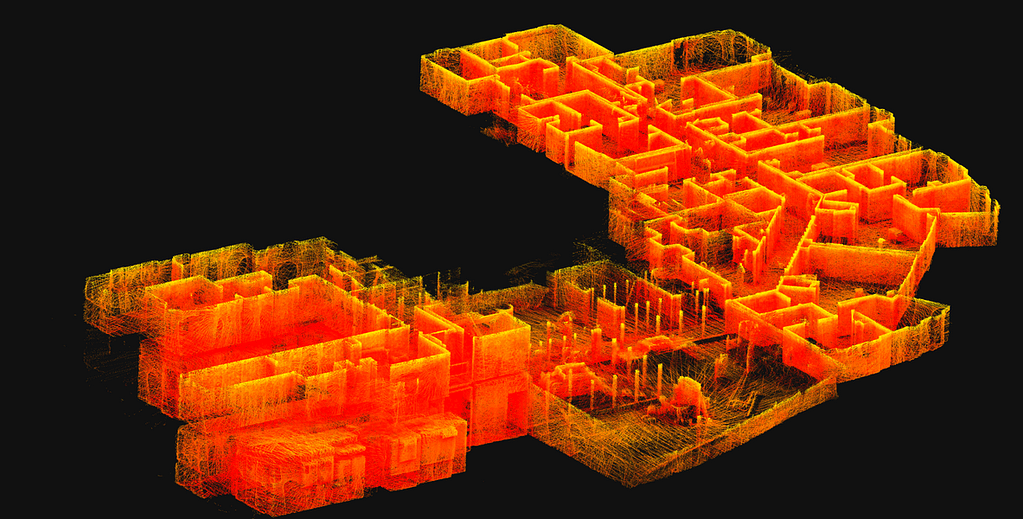
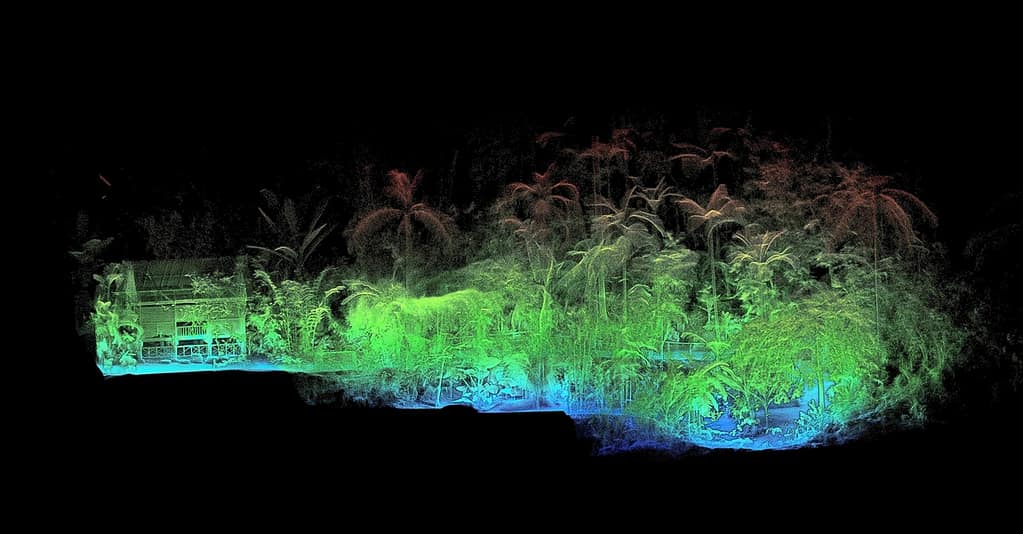
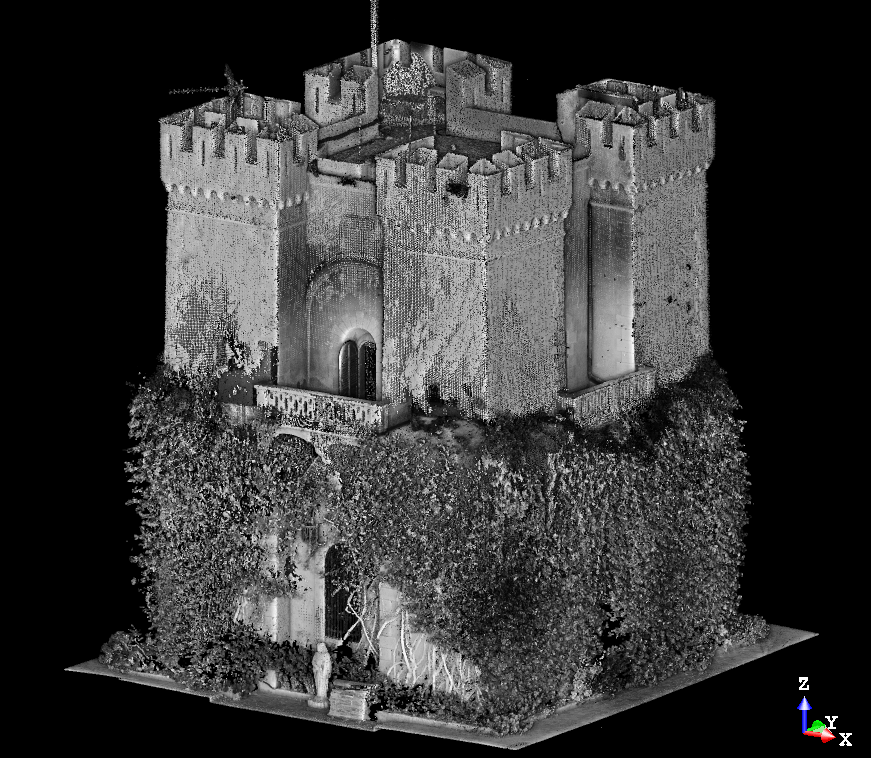
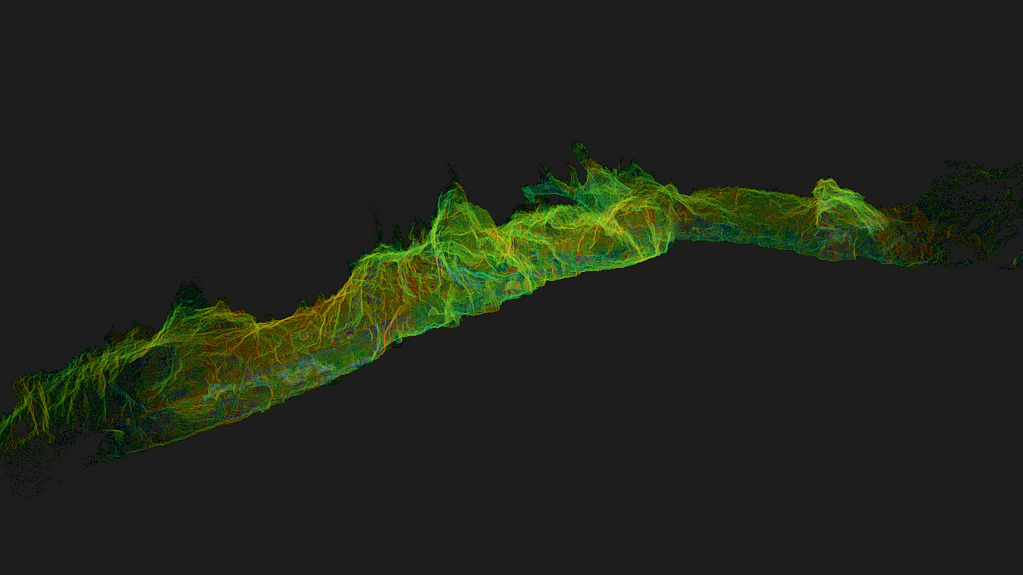

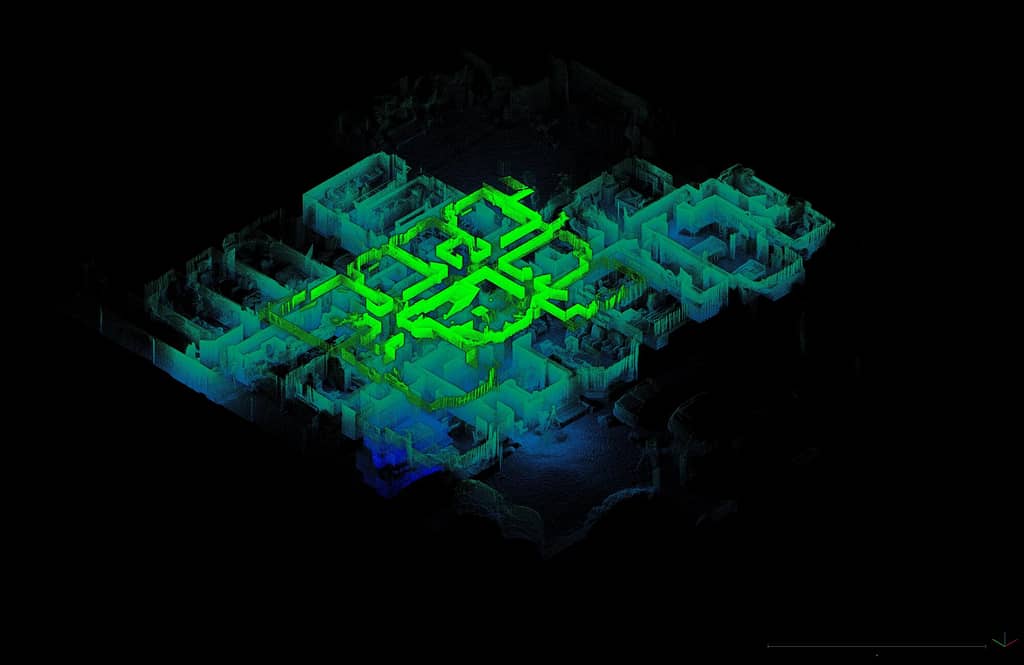


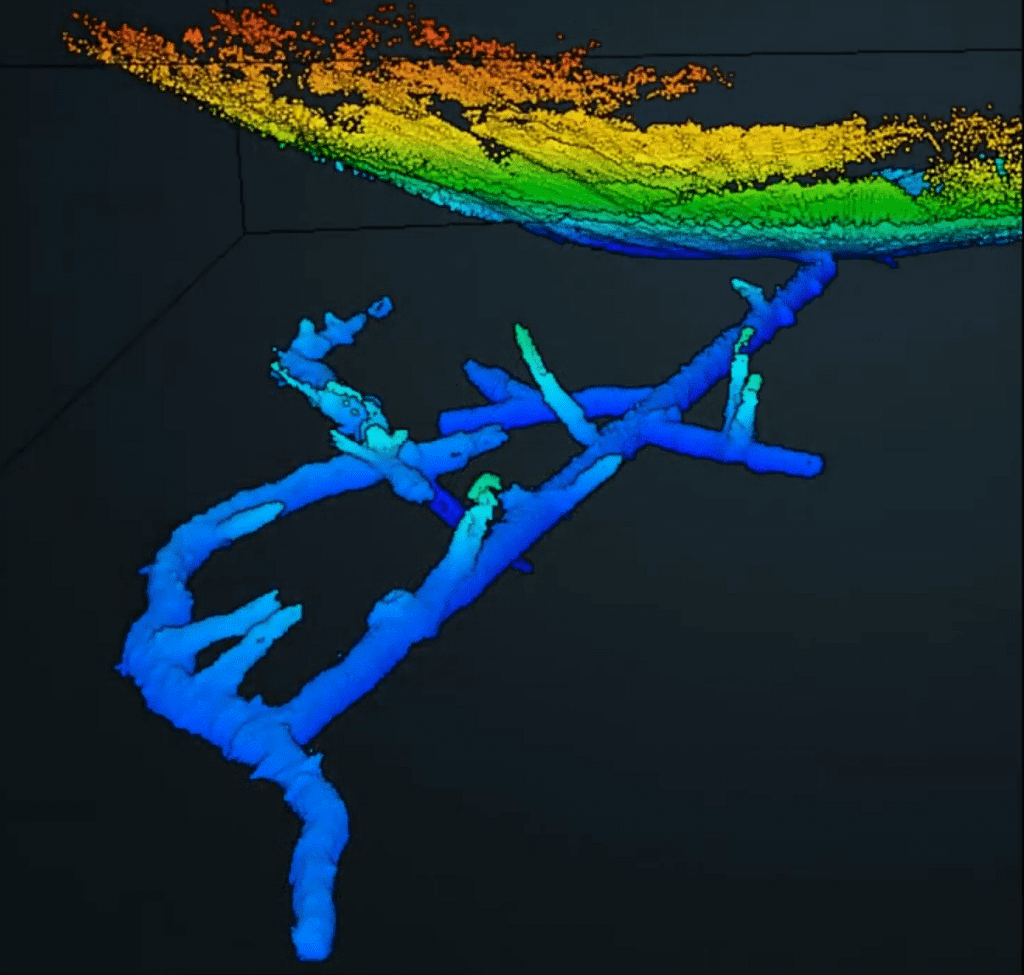
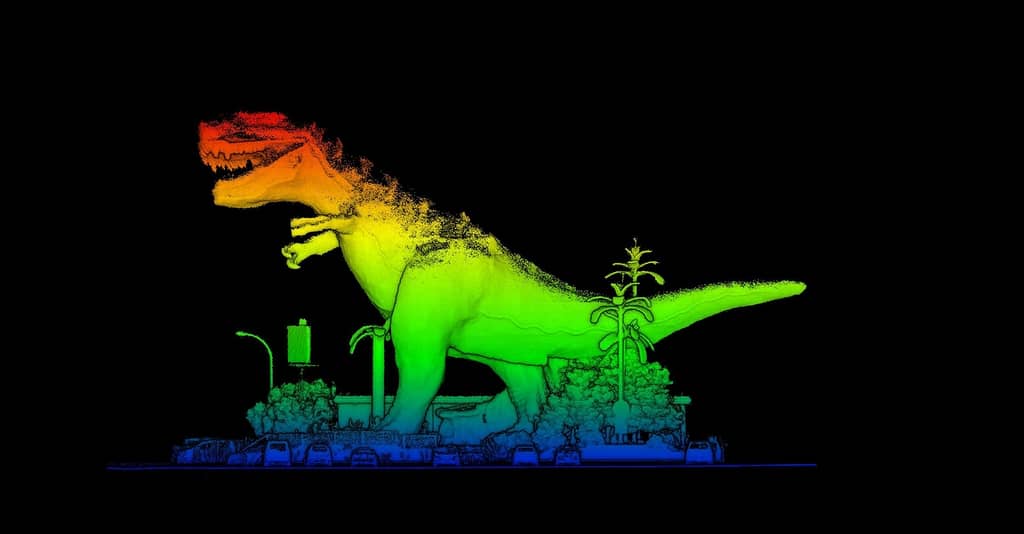

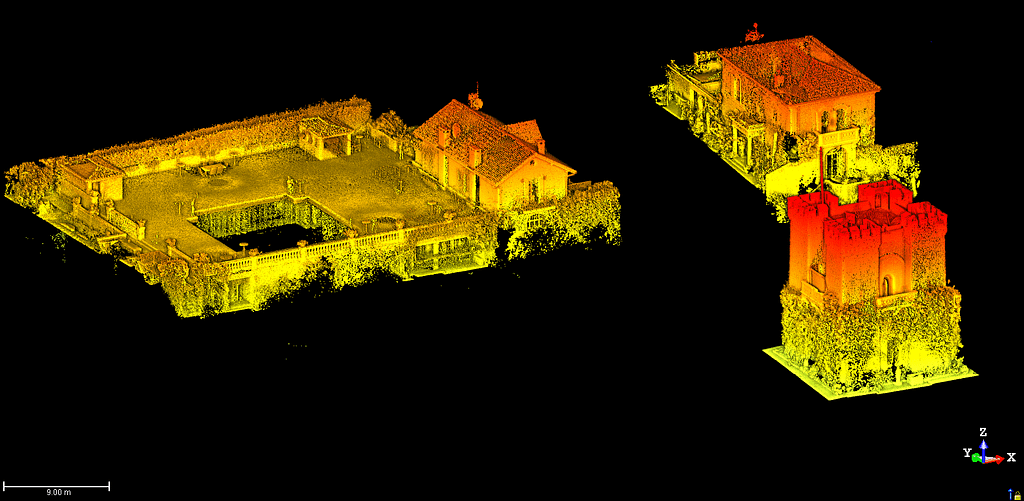
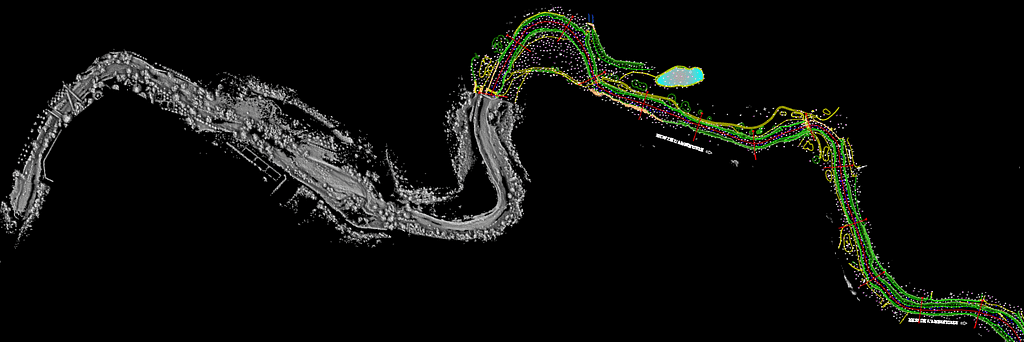
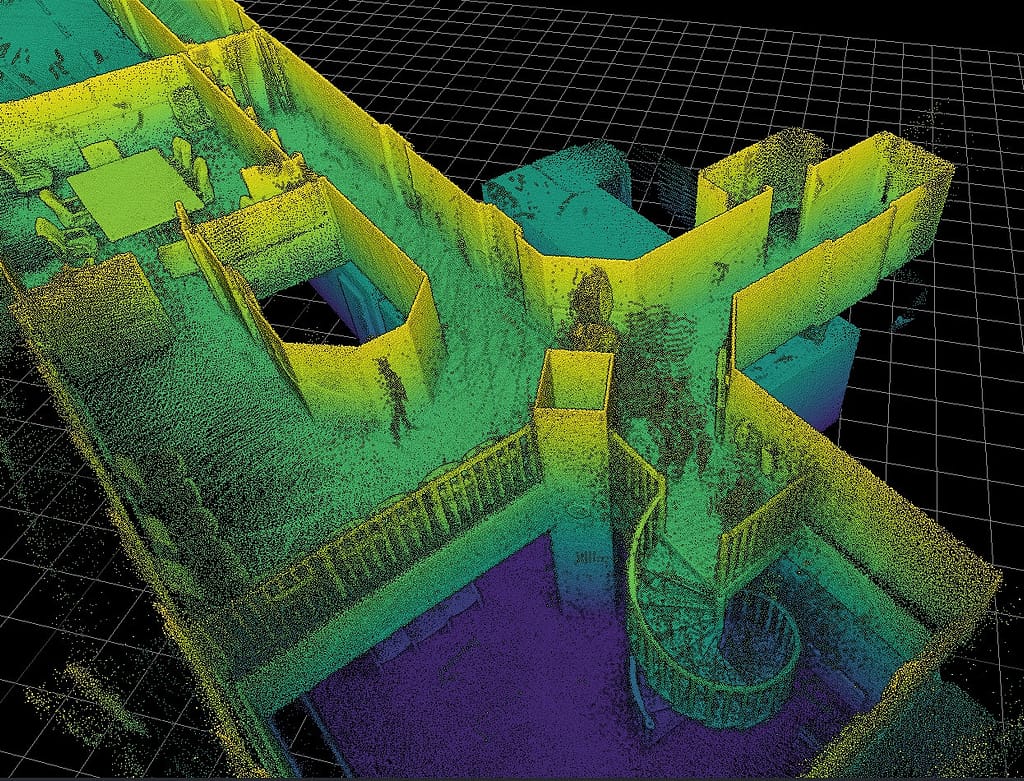
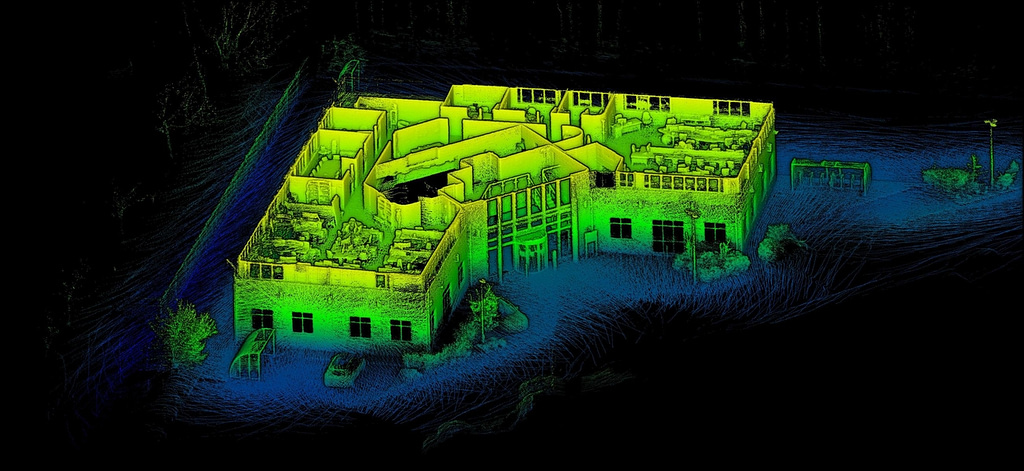


What does LiDAR data show?
What is shown in your data will depend on what you scan. Data will include all the points that pertain to different aspects of your LiDAR scan. This could be the ground, vegetation, an object, building, room or anything else detected by laser scanning.
Learn more about the Christ the Redeemer scan here.
See the full case study for this scan here.
How is LiDAR data processed?
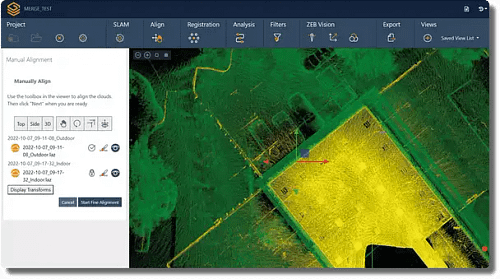
Software like GeoSLAM Connect can make processing LiDAR data easy. Your results can be automatically processed using pre-defined workflows. Advanced users can also write their own custom processing instructions.
Once your data is captured, it is then processed using our leading SLAM algorithm. SLAM (or simultaneous localisation and mapping) allows a device to locate itself whilst creating a map of the area. This is what enables mobile mapping and helps you map places that are traditionally hard to reach with GPS.
GeoSLAM Connect can integrate with various software to help you interpret, visualise and inspect it in more detail. You can combine LiDAR data with other data types like vector data, CAD, GIS and more to create something that’s easy to recognise and view.
How can I see LiDAR data?
To read your LiDAR data, you’ll usually need software like GeoSLAM Connect. However, you can view LiDAR data in real time with our ZEB Revo RT. This device has the capacity to process data quickly and so you can see the point cloud as you walk.



What can you do with LiDAR data?
Commonly used across a whole host of industries, there are many applications of LiDAR data. Point clouds are really versatile and can provide a rich source of information in so many different circumstances. Here’s a brief overview:
Mapping: LiDAR systems can be used to create Digital Terrain Models (DTMs) of the bare earth or Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) which include both the ground surface and all the objects within the space.
Forestry: laser scanning is popular for forestry, allowing data collection for the monitoring of canopy height, vegetation and forest preservation.
Architecture, Real Estate & Construction: it’s simple to gather data on buildings which can be used for construction, building restoration, creating floorplans and much more.
Mining: scanning underground and even potentially dangerous areas can be achieved with this technology. Mine shafts can be monitored and inspected to maintain a safe working environment.
You can find out more information on how to use LiDAR in our dedicated article ‘what is LiDAR?’
Is LiDAR technology safe to use?
Yes, the lasers used in GeoSLAM LiDAR scanners are Class 1, which means it is eye-safe under all operating conditions.
How can I download LiDAR data for free?
Sources of free LiDAR data are few and far between. We have a collection of free LiDAR data that you can view and download in our sample data area. You can see point clouds of some famous landmarks, caves and buildings for yourself. This gives you free access to some example LiDAR data, helping you understand how this technology is used to measure, map and explore spaces.