Last Updated on 16th May 2023
A variety of industries rely on laser scanning. Construction companies are using it to speed up surveying processes, and engineers are using it to streamline digital work. Even ecological conservationists and historians are relying on the mobility of scanners and the versatility of point cloud data. This popularity is not limited to the practical or industry side. Educational institutions are turning to LiDAR scanners to help too. Laser scanning in education is not just for research, but to enrich their teaching.
In this post, we’ll look at the ways that departments are exploring the benefits that laser scanners bring to education.
What is the use of laser scanners in education?
The next generation should always have an opportunity to experience existing and emerging technologies. It will help them grasp important concepts during their studies and prepare them for the day-to-day work after graduation. The sooner they start getting hands-on experience with these tools the better. It will enhance their own learning experience and benefit the technology.
Students will be tomorrow’s innovators. They will find new ways to use 3D scanning technology and spot its potential. But to do this they need experience with the scanners and LiDAR. To generate ideas and identify new uses, they need to be comfortable with the current ones.
What benefits and challenges are there when integrating laser scanning in education?
There are obvious benefits to using 3D scanners as an educational tool. From classrooms to fieldwork and long-term research, scanners have a range of uses. But there are also challenges.
If you’re wondering what mobile laser scanners can add to your curriculum, here’s a quick rundown of things to consider.
Benefits
Staying at the forefront of industry developments
It is important that higher education embraces new technologies. As well as offering experience with them, they need to innovate new uses and applications. This attracts students and impresses funding boards.
A lot of the developments in the uses and capabilities of laser scanning are down to universities. Yet there is still potential for more. It could push boundaries for research projects, earning funding and enhancing reputations.
Investing in the latest technologies shows potential students that the institution is committed to giving a high-quality teaching and learning experience.
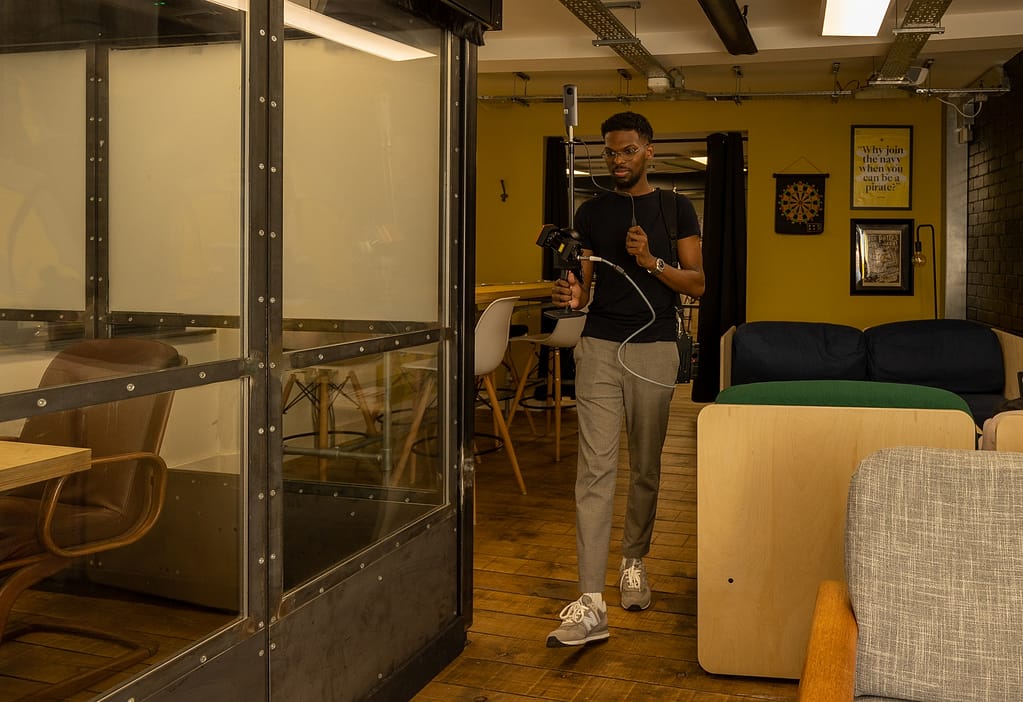

Improving student’s employability prospects
When preparing students for the world of work, it is important to equip them with as many relevant skills as possible.
In many industries, the regular use of mobile laser scanners is turning them into essential equipment. They make a variety of tasks quicker while opening up possibilities with the digital design process.
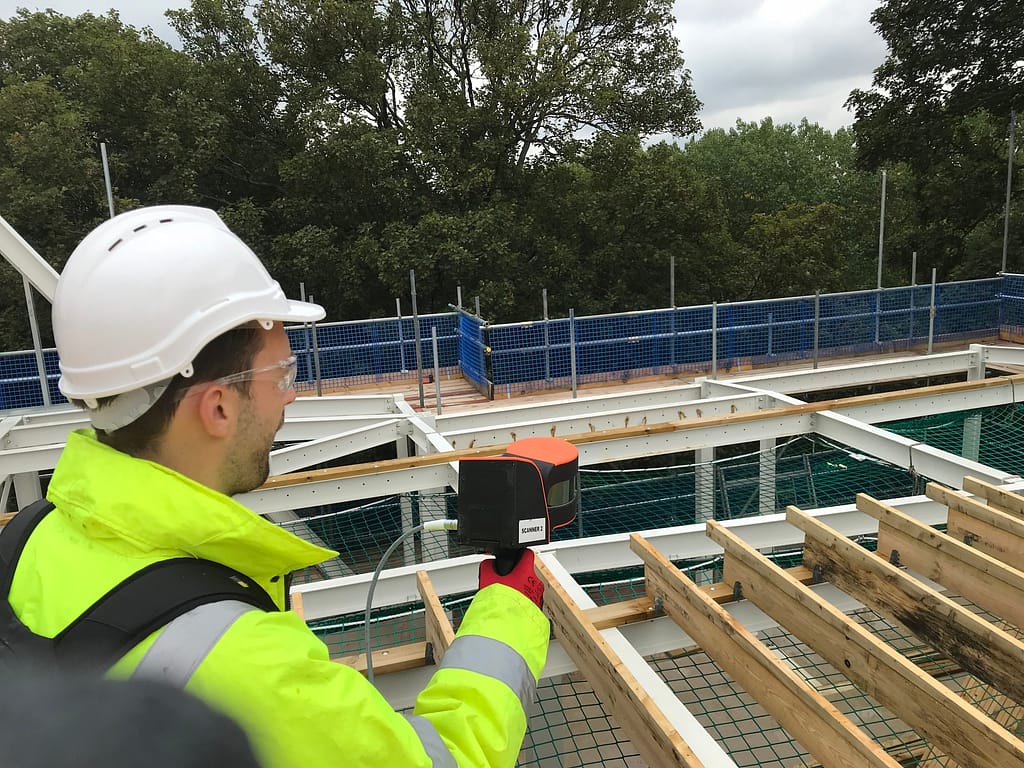

Increasing engagement with hands-on experience
Getting hands-on experience with a laser scanner is a great way to increase engagement in ways your teaching team will already appreciate.
Using the scanner itself will give students a practical learning experience and create a sense of student empowerment. The point cloud data they collect will bring a whole new raft of benefits, allowing them to access the ‘create’ level of learning when applying what they have been taught.

Challenges
Cost
Research and development in laser scanning technology have reduced costs over recent years, opening the possibility for educational institutions to purchase scanners rather than rent them.
Skills
Mobile laser scanners and other equipment are built with usability in mind. Some, like our own ZEB scanners, are simple enough to use with minimal training.

Integration
In the past, it may have been difficult to use point cloud data without the correct software to process and analyse it. This is no longer the case, with integration often a key priority in the design and development of scanning equipment.
Laser scanning in Education: Making the most of laser scanners is about more than just getting access to the hardware – you need the software to back it up too. With GeoSLAM Classroom licensing, we offer discounts on mobile laser scanners and licensed software to help make GeoSLAM technology affordable and practical.
Universities that invest in LiDAR scanners and software help their facilities lead the way and give their students a better learning experience.
Case Study
Digital Technologies in Heritage Conservation at Bamberg University
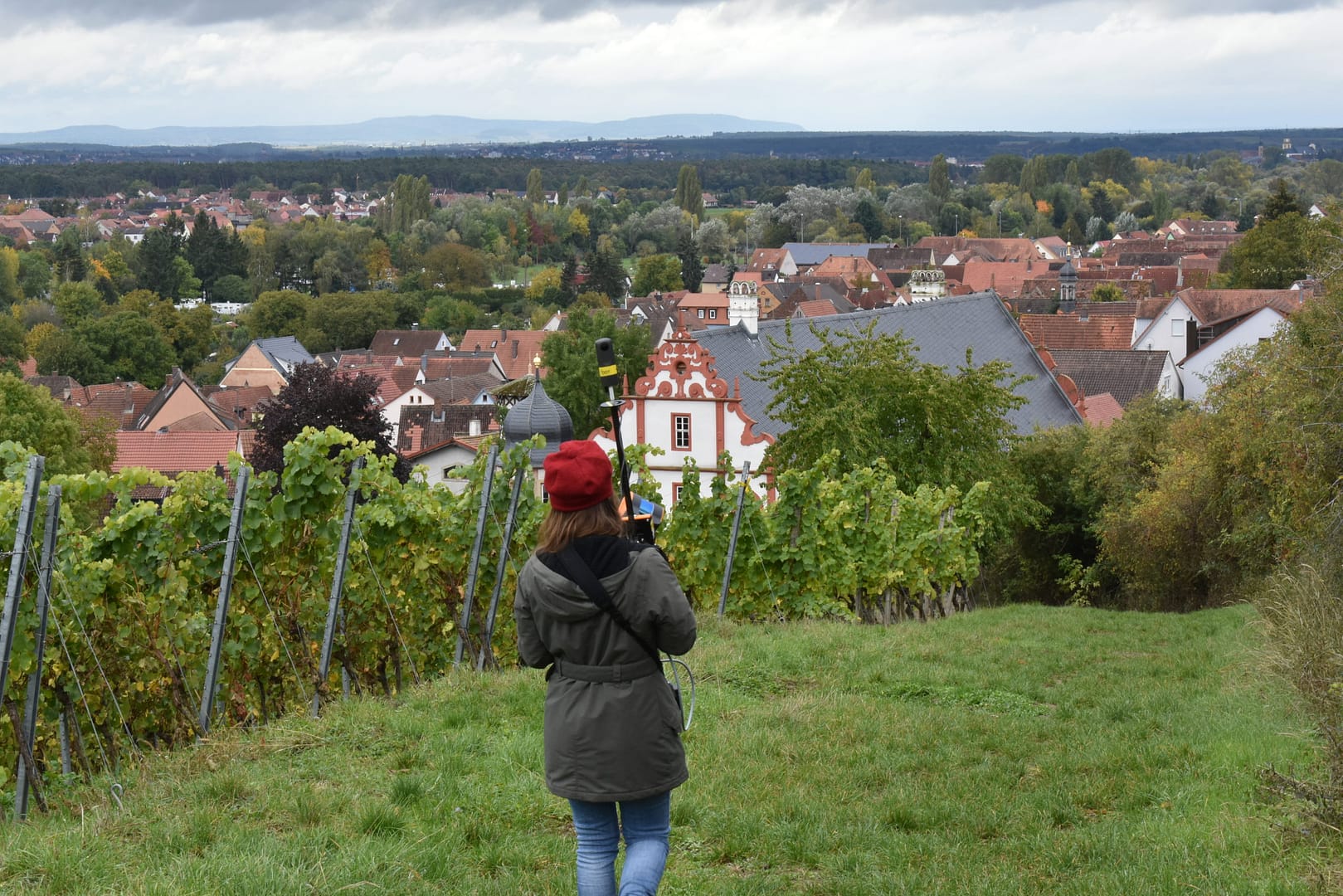

Which areas are using laser scanners in higher education?
With many possible uses for laser scanning in education, it’s unsurprising to see a range of faculties making use of the technology. As well as core topics in engineering and the built environment, a broad group of humanity and science subjects are able to explore important concepts outside the classroom using scanners.
Here are some examples of the different ways various departments have already used laser scanners and the benefits they’ve gained.
Architecture, Engineering and Built Environment
LiDAR scanners are an essential tool for measuring, mapping and establishing the conditions of existing infrastructure. The increased use of handheld scanners on-site means it’s important that students know how to use them.
During the construction process data can chart changes and progress, and even monitor resources and stock throughout a project.
What technology do you need to be an architect?
Architects focus on the planning and design process, relying on surveyors to bring in information on existing structures and spaces. The simplicity of handheld LiDAR scanners takes away this need. It allows architects to do every part of the job themselves, saving time and money, even on complicated jobs.
How does technology help in engineering?
The engineering industry has embraced mobile laser scanning as a quick, reliable way of collecting accurate data. The mobility of these scanners means that data acquisition is a lot faster. Therefore, they are safer because surveyors don’t need to spend prolonged periods of time on site.
What is the future of land surveying?
Handheld LiDAR scanners are likely to become a vital part of land surveying in the future. They offer a fast and simple way to capture complicated data without laborious setups.
Giving students knowledge of mobile LiDAR scanners will give them an edge when they come to work in the industry.
Geology, Geography and Environmental Sciences
When it comes to scanning hostile environments or complex natural formations, the fast set-up and mobility of scanners are vital.
Universities and research centres aren’t just restricting this technology to their teaching staff. Students are getting the chance to use it too.
Here are some ways that ZEB scanners support staff and students in their research.
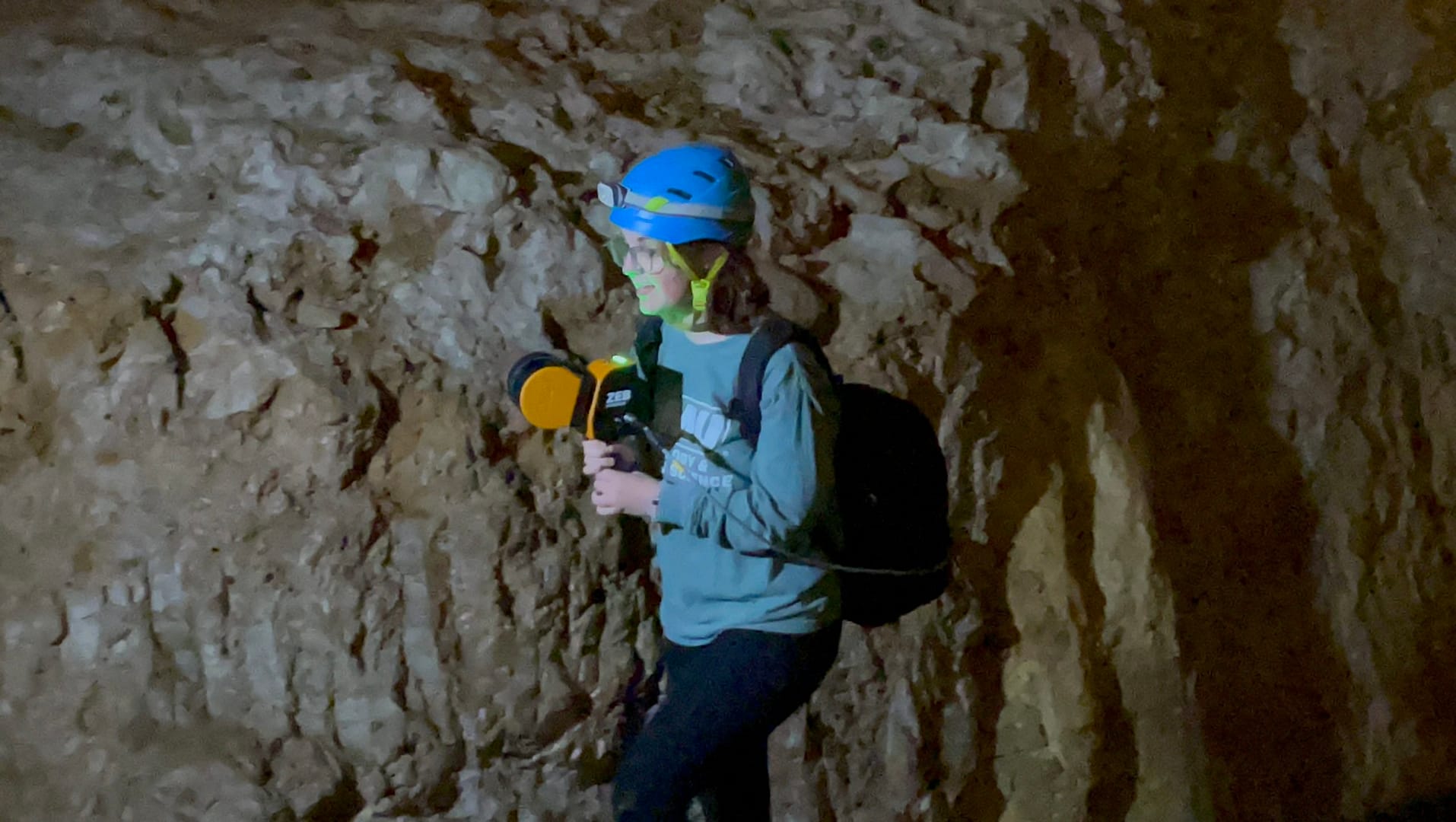
Case Study
Scanning Grand Caverns with James Madison University

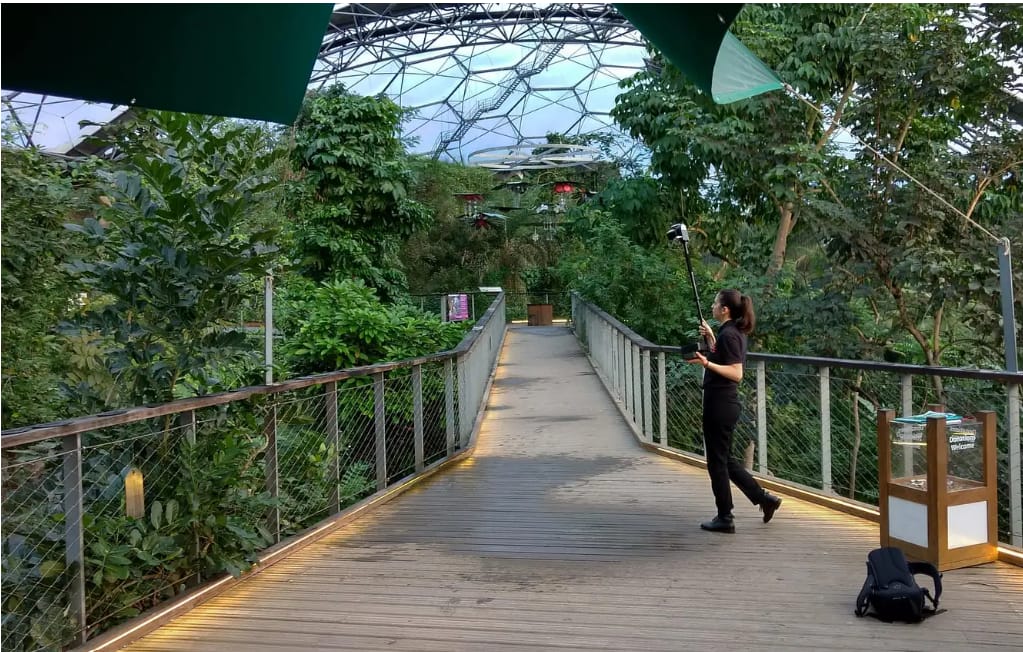
Case Study
Understanding Forest Environments with the University of Leicester

History and other humanities
3D laser scanning on historical preservation is redefining historical study.
Handheld laser scanners makes the process of mapping restrictive, delicate and detailed historical sites far quicker than previous scanning techniques. The ease of use means that staff and students can collaborate on projects, so students gain valuable field experience. Their contributions are often added to the important research.
The impact of laser scanners is not limited to field research when it comes to historical studies though. Universities and institutions are using point cloud data gathered to create 3D models and AR or VR versions of historic sites.
This brings long term benefits for future generations inside and outside of the universities carrying out the research.
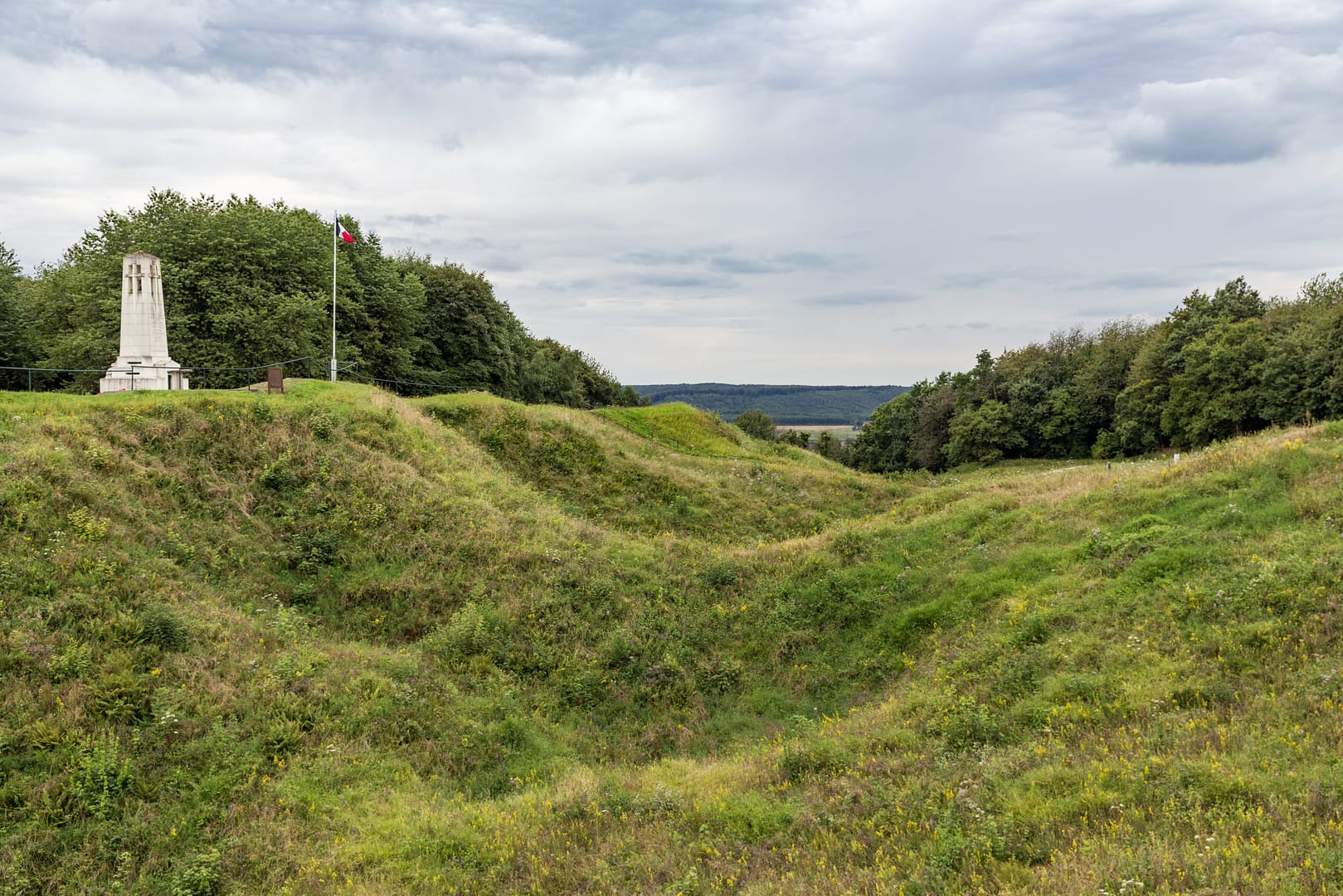
Case Study
Virginia Tech University Scan the Vauquois Tunnels and WWI Battlefield

Other educational uses for laser scanning
Technical hardware like scanners is usually focused on research and teaching, however there are no real limits to its use. One scanner within a university could be used across several departments making them a cost-effective solution.
GeoSLAM technology has been used for mapping both Exeter University and Oxford University. Mobile scanners generated high-quality point cloud data across major areas of the sites without causing disruption to the working campuses. In both these situations, work was completed by external bodies but once the technology is owned in-house, the wide range of applications is open to anyone.
ZEB Horizon scanners were used as part of a psychological and physiological study by The Human Adaptation Institute. The Deep Time 40 experiment isolated their team in a cave for 40 days to test their ability to adapt. During this experiment, they were given tasks to help structure their days – starting with scanning the caves. The simple set-up and ‘walk and scan’ capabilities created an engaging task that played a key role in the experiment.
What is the use of laser scanners in education?
In conclusion, we draw back to our original question – what is the use of laser scanners in education? The answer is both clear and complex because the uses are almost limitless in both subject areas and applications.
From enabling student empowerment through work-based skills to increase engagement through hands-on tasks. The possibilities for the use of scanners in education are endless.
On-demand Webinar
GeoSLAM for Education
Want to know more? Watch this webinar in your own time to learn how educational institutions are inspiring the next generation of surveyors using GeoSLAM handheld LiDAR scanners.
Hear from three guest speakers from different Universities and Colleges across the world discussing their own individual experiences uses handheld LiDAR scanners to support education and inspire their students.