Last Updated on 28th July 2023
Mobile LiDAR technology has had a positive impact in construction site surveys, offering remarkable efficiency and accuracy. Combining the power of laser scanning with versatility, mobile LiDAR systems provide a comprehensive representation of the environment in record time. This innovative approach reduces the need for traditional survey methods, reducing costs, minimising human error, and advancing project timelines.
This article explores some of the various ways that mobile LiDAR data has improved construction site surveying.
Site survey challenges in construction
Construction site surveys play a crucial role in the planning and execution of Architecture, Construction, Engineering (AEC) projects. However, traditional surveying methods often encounter challenges that can hinder a project. Here are a few examples of the challenges construction sites face when conducting surveys:
Time Constraints
One significant challenge in construction site surveying is the time-consuming nature of traditional surveying methods. Conducting surveys manually requires extensive fieldwork, often involving multiple surveyors and an arsenal of equipment. This can result in delays, especially when projects have tight schedules.
Inaccessibility and Hazardous Environments
Construction sites are often characterised by challenging terrain, restricted access, and hazardous environments. Though safety precautions are in place in most countries, there is always the potential risk to personnel. Therefore, regular data collection can be a daunting task for surveyors spending large amounts of their time recording information. Mitigating this risk by reducing or eliminating the amount of time needed on site is another step forward to ensuring personnel safety.
Complex Buildings and Structures
Construction sites frequently feature complex structures, such as buildings, bridges, or road networks. The intricate designs often require precise measurements and detailed documentation for accurate planning and execution. Manual methods of surveying may struggle to capture these complex environments accurately. Static LiDAR technology has the capacity to provide accurate and granular datasets, however, it requires many setups in potentially unforgiving environments, risking gaps in the data. Utilising real-time data feedback from mobile LiDAR scanners, like the ZEB Horizon RT, can improve confidence that the entire capture area is captured.
Data Accuracy and Precision
Data accuracy and precision are one of the most important aspects of construction site surveys. Removing the traditional methods for data capture, which are prone to human error, is key for getting consistent objective data. Capturing reliable datasets and repeatable scanning solves this issue and provides key stakeholders with the most up-to-date and accurate information available.
Surveying methods have changed and continue to change as old technologies innovate and with the introduction of new technologies. The construction industry isn’t always quick to adopt new technologies, however, by doing so could save money, time, and face down some of the challenges set out above.
The progression of site surveying technology
The past few decades have seen many industries change their workflows due to the rapid growth of new technologies, and AEC is no different. Construction site surveying has experienced a remarkable transformation due to cutting-edge technologies like LiDAR.
Building Information Modelling
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is now a critical component in the field of construction site surveying and offers significant advantages when integrated with total stations or LiDAR technologies. BIM is the collaborative process that involves creating and managing digital representations of a construction project’s physical attributes. BIM offers a wide variety of benefits including design integration, clash detection, cost estimations, construction monitoring for stakeholders, and facilities management.
The integration of BIM into an AEC workflow has enhanced the process of seamless collaboration.
Total Station and robotics
The history of total stations tracks back to the early 20th century, with the development of the first Electronic Distance Measuring (EDM) instruments. The integration of EDM and electronic theodolite technologies gave rise to total stations. Total stations enabled surveyors to measure angles, distances, and collect data in a single device. Further innovations to the total station in the 1980s the led to the development of robotics. Robotic total stations further automated the process by allowing surveyors to control the instruments remotely, reducing the time required for data collection on construction sites.
Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS)
Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) brought a ground-breaking shift to surveying when it entered the world of engineering in the 1990s. TLS systems emit laser beams to capture millions of points in a scanned area, generating a highly detailed 3D model known as a point cloud. TLS technology revolutionised the surveying process by enabling rapid data acquisition from a fixed position, precise as-built documentation, and comprehensive analysis of complex structures. Even today, static based laser scanners, like the FARO Focus, continue to innovate and dominate the AEC market, providing unrivalled accuracy and granular data.
UAV and ground drones
Over the past decade the UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) market has boomed for both commercial and recreational use. One commercial use, for various industries, is surveying. Equipped with high resolution cameras or LiDAR sensors, drones have the capacity to capture data of large sites fast. They also have the advantage of taking the surveyor out of harm’s way, by controlling them in a safe location. Drones have been instrumental for capturing data in inaccessible areas, enabling more efficient project planning and monitoring. In addition to drones, autonomous vehicles like Ghost Robotics Vision 60 ground drone mounted with LiDAR, provide an avenue for capturing internal data without the need for the surveyor to enter a building.
What is mobile LiDAR and SLAM?
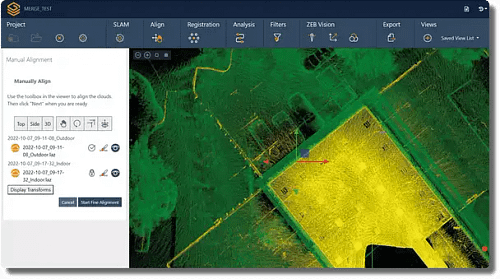
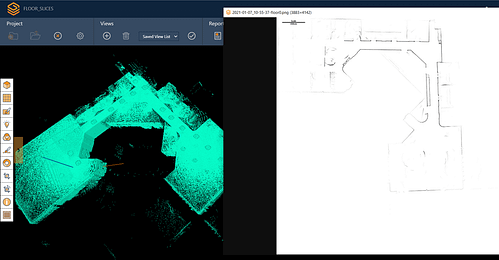
Mobile LiDAR has quickly become an indispensable tool in the AEC industry, enabling professionals to obtain precise measurements, create highly accurate 3D models, and streamline the planning and execution of construction projects. Born out of complex SLAM (Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping) algorithms and like TLS, mobile LiDAR data provides a highly accurate 3D point cloud. Unlike TLS, it works at its best when it is in motion, relying on features in the environment to confidently map an area. Additionally, mobile LiDAR’s lightweight nature and lack of need to be in a fixed position make it one of the most versatile solutions for surveyors currently.
How does mobile LiDAR improve construction site surveying?
Mobile LiDAR technology significantly improves construction site surveying in several ways, revolutionising the efficiency and safety of the process. Here are some key examples where LiDAR has proven to be beneficial:
Clash detection
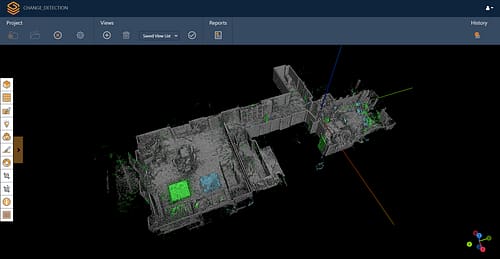
Clash detection is an important part of surveying because it helps to identify clashes or conflicts with building components, helping to prevent reworks. Mobile LiDAR provides highly accurate and detailed 3D data that can be overlaid with the building design models created in BIM software. By comparing the two datasets, potential clashes between the design and existing site conditions are detectable early. This allows for proactive resolution of clashes, minimising rework, and avoiding costly delays during the construction process.
Site planning and optimisation
Mobile LiDAR captures detailed information about the topography, existing structures, and utilities of a construction site faster than traditional methods. This data leads to better site planning and optimisation. Gathered 3D data is ideal for identifying the most suitable locations for buildings, roads, or utilities. Optimising the site layout and planning improves construction efficiency, reduces material waste, and enhances the productivity of the project. Additionally, easily repeatable data capture with mobile LiDAR provides up-to-date data of the site, to compare with original plans, as often as needed.
3D modelling and simulations
The use of 3D models and simulations is ever more prevalent in AEC, for a variety of reasons. For instance, the 3D models generated from mobile LiDAR can highlight energy deficiencies in a building through techniques like sunlight and shadow analysis. Architects can take accurate information from existing buildings to better optimise them in renovation projects. Virtual walkthroughs are also another great example where mobile LiDAR is a useful tool. Allowing stakeholders access to the site, as often as needed, without the need to travel there.
Improved accessibility
Mobile LiDAR improves accessibility in construction by enabling remote data collection, through its versatility. It allows surveyors to capture data from challenging or hazardous areas while maintaining their safety. Providing comprehensive and accurate, mobile LiDAR enhances accessibility for future projects, maintenance, and operations, leading to better decision making.
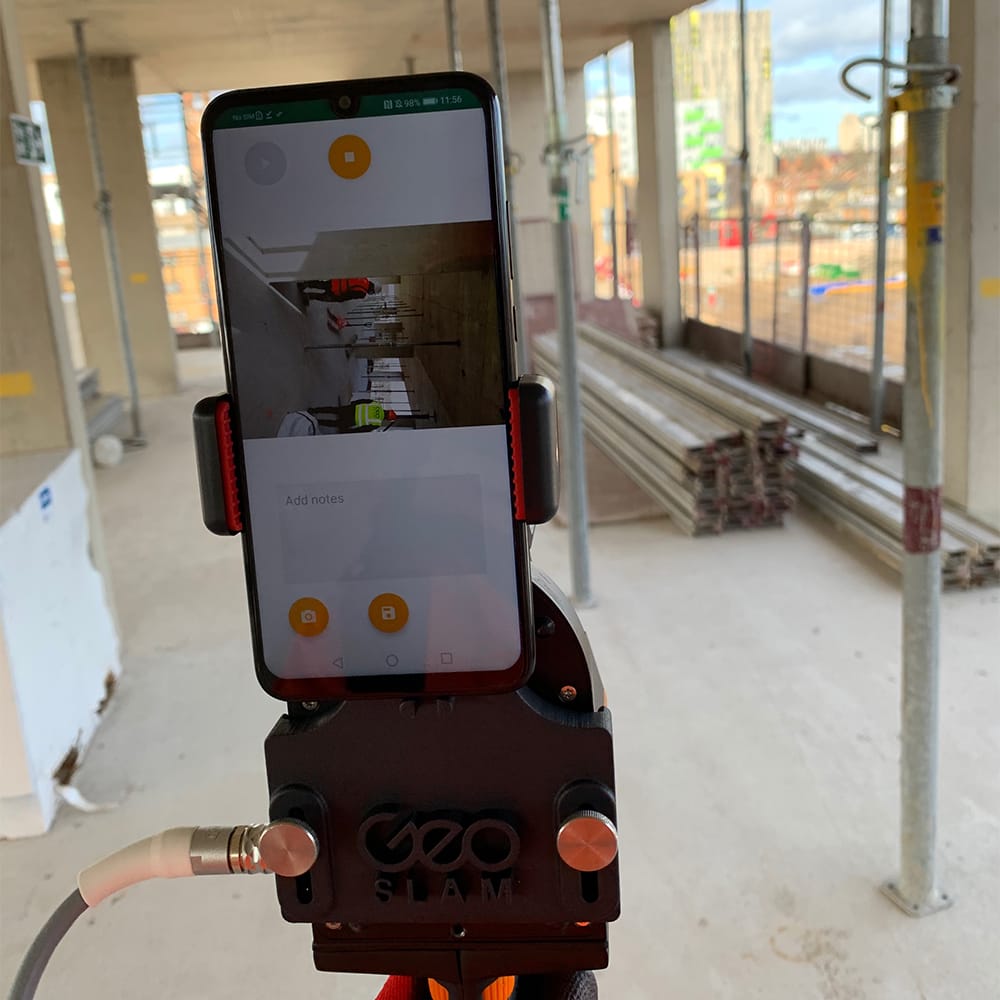
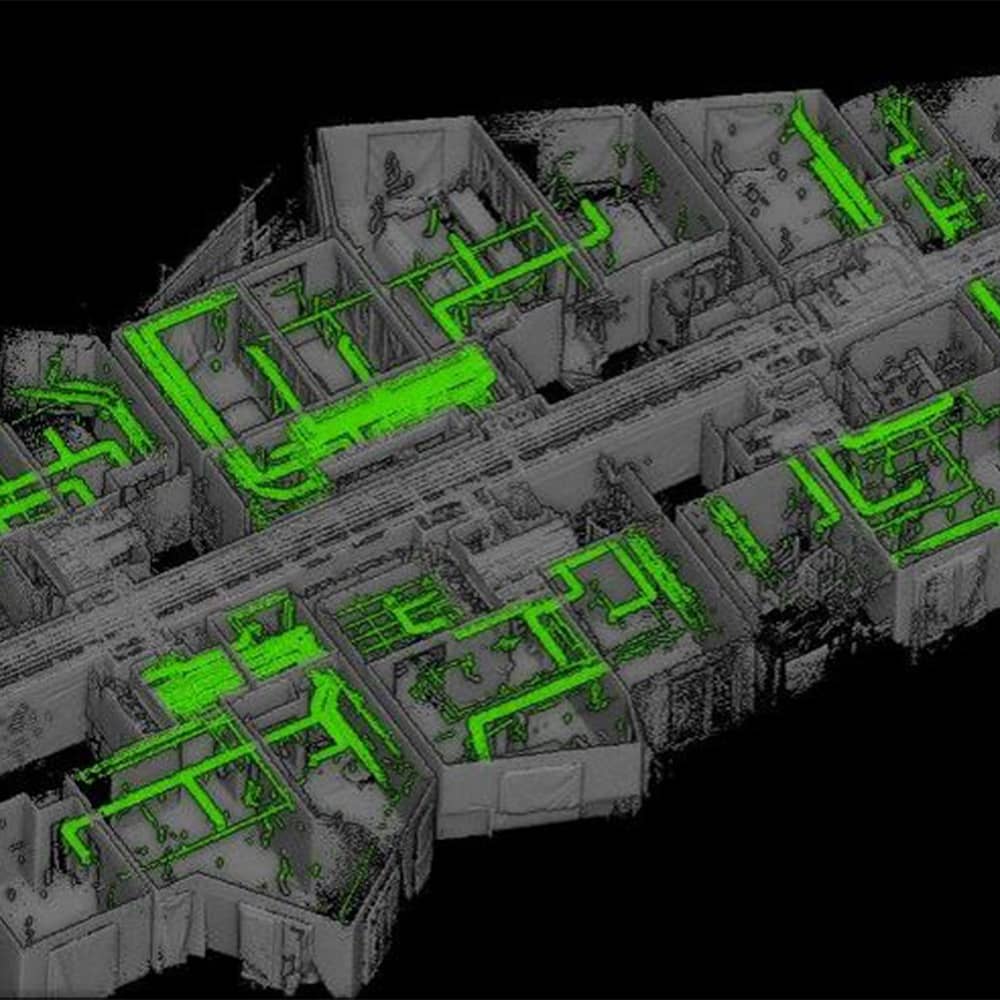
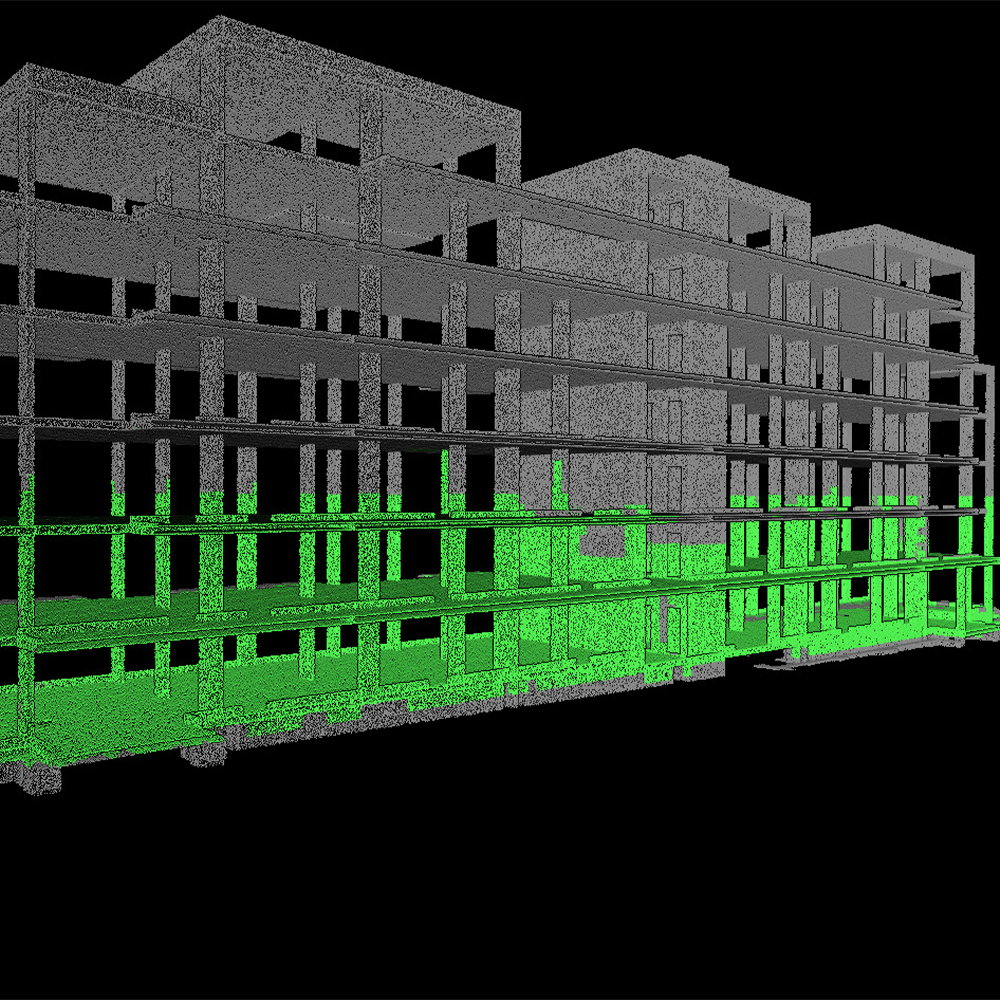


How is mobile LiDAR different to other forms of data capture?
The variety of methods stated above for capturing data are all valid for various reasons, and often work together to complete a task. Mobile LiDAR seeks to provide a single tool with the capacity to comprehensively complete numerous tasks, to an extremely high standard. Mobile LiDAR tools, like the ZEB Horizon, offer the following:
Speed
With 300,000 scanner points per second, it’s fast work scanning both simple and complex environments. You can carry out high-quality scans in less time.
Portability
Light weight and portable, you can move freely whilst using this device. This portable 3D scanner features a rotating LiDAR sensor for the widest field of view. Its compact size and ergonomic design make it a delight to use.
Accuracy
The ZEB Horizon provides 3D scanning with a survey grade relative accuracy of up to 6mm dependant on the environment. This gives you accurate scans and fine details.
Versatility
With a range of 100m, the ZEB Horizon is our most flexible 3D laser scanner yet. Use it outdoors, indoors or underground. Mount it to a drone, a backpack or a vehicle.
The future of the construction industry with mobile LiDAR
The wave of new technologies and advancement in old technologies in all industries is leading to a bright future for surveying. Mobile LiDAR has had a huge impact in the past decade, becoming more readily available, versatile, and cost-effective, and this continues to grow year on year. Surveyors looking to optimise their construction site surveys and provide various services using one tool need not look any further than mobile LiDAR and its equally bright future.
Get in touch
If you’d like to learn more about how GeoSLAM solutions can help you, submit the form below.